In this project tutorial, we’ll create an Arduino Fading LED Project using PWM (analog output). You’ll learn how PWM works, and how to create a LED Fading effect with Arduino (Fade-in and Fade-out effects). And we’ll simulate and run the project code example to test its functionality. Without further ado, let’s get right into it!
Table of Contents
- LED Fading With Arduino
- Fading LED Project Wiring Diagram
- Arduino Code – LED Fading
- Fading LED Project Simulation
- LED Fading Project Testing
- Project Wrap Up
LED Fading With Arduino
To create the Arduino Fading LED project, we need the following components:
- Arduino Board
- LED
- Resistor (330Ω)
The Arduino Fading LED Effect is based on the Arduino PWM output signal that’s used to control the LED brightness and gradually increase and decrease its duty cycle to achieve the LED Fading effect.
Arduino boards have several PWM output pins usually. Those pins are designated with a (~) mark next to the pin number on the board. Before discussing how to use the PWM output pins, let’s first define what is the PWM technique and what are the properties of a PWM signal.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique for generating a continuous HIGH/LOW alternating digital signal and programmatically controlling its pulse width and frequency. Certain loads like (LEDs, Motors, etc) will respond to the average voltage of the signal which gets higher as the PWM signal’s pulse width is increased.

As you can see, the LED gets brighter as the pulse width (duty cycle) increases, and it gets dimmer as the pulse width decreases. And this is typically what we use the PWM output for.
Check the tutorial below to learn more about Arduino PWM. It’s a prerequisite for this project to help you understand the topic in more detail.
This tutorial will provide you with more in-depth information about Arduino PWM output. Starting from the basics of PWM signal, its frequency, duty cycle, and resolution, and will discuss in detail how it works and how to use it in various Arduino control projects.
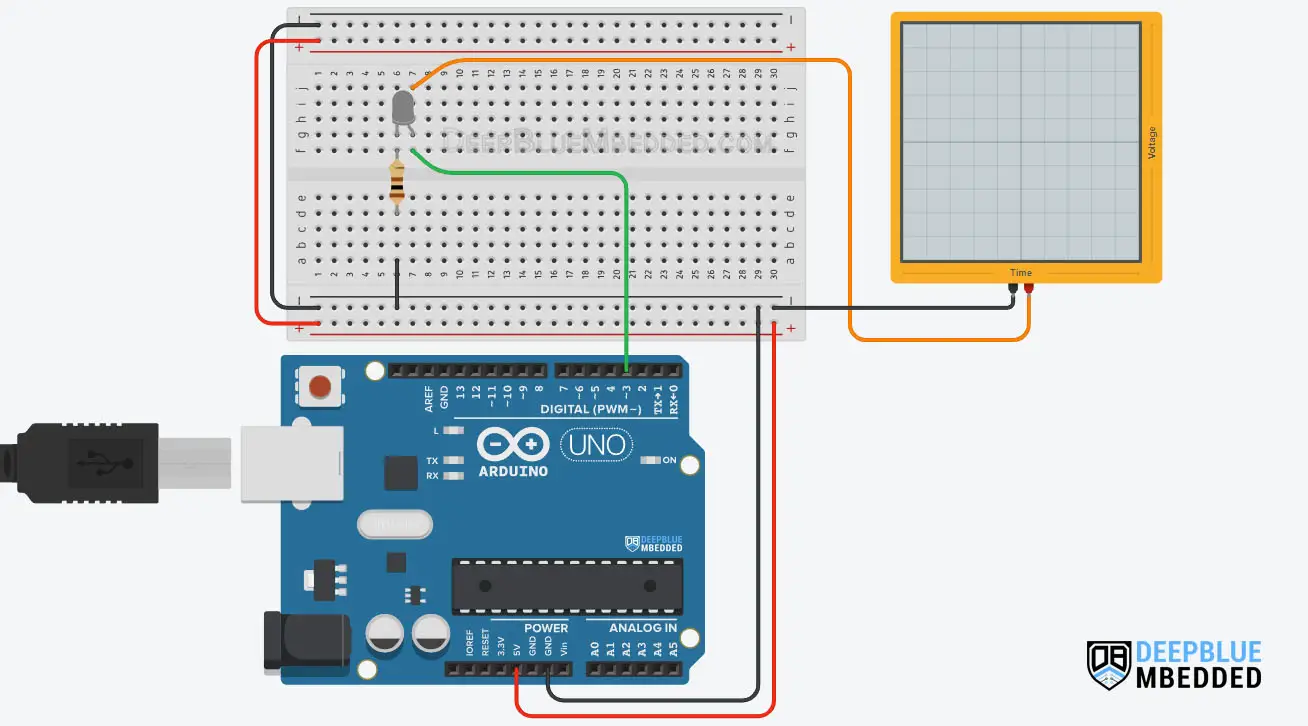
Fading LED Project Wiring Diagram
Here is the wiring diagram for this example showing how to connect the LED output and the oscilloscope channel.
Arduino Code – LED Fading
In this example project, we’ll control an LED brightness with an Arduino PWM output pin. Using two for loops, we’ll gradually increase the duty cycle from 0% up to 100%. Then, gradually decrease it from 100% down to 0%. And keep repeating!
Here is the full code listing for this example.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
/* * LAB Name: Arduino PWM LED Fading Example * Author: Khaled Magdy * For More Info Visit: www.DeepBlueMbedded.com */ #define LED_PIN 3 void setup() { pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); } void loop() { // Gradually Increase Duty Cycle for(int i=0; i<255; i++) { analogWrite(LED_PIN, i); delay(5); } // Gradually Decrease Duty Cycle for(int i=255; i>0; i--) { analogWrite(LED_PIN, i); delay(5); } } |
Code Explanation
First of all, we define the IO pin used for the LED output. It has to be a PWM-enabled IO pin (for UNO: 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, or 11).
|
1 |
#define LED_PIN 3 |
setup()
in the setup() function, we’ll set the pinMode to be output.
|
1 |
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); |
loop()
in the loop() function, we’ll create 2 for loops. The first for loop will gradually increase the output PWM’s duty cycle with a small 5ms delay time after every PWM duty cycle update operation. And that’s the Fade-in Effect implementation.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
// Gradually Increase Duty Cycle for(int i=0; i<255; i++) { analogWrite(LED_PIN, i); delay(5); } |
The second loop will gradually decrease the output PWM’s duty cycle from 100% down to 0%. Which is the Fade-out Effect implementation. And everything will keep repeating forever.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
// Gradually Decrease Duty Cycle for(int i=255; i>0; i--) { analogWrite(LED_PIN, i); delay(5); } |
Fading LED Project Simulation
We can test this project’s code example using any available Arduino simulator environment. Here I’ll show you the simulation results for this project on both TinkerCAD and Proteus (ISIS).
TinkerCAD Simulation
You can check this simulation project on TinkerCAD using this link.
Proteus (ISIS) Simulation
Another extremely powerful simulation environment for Arduino is the Proteus (ISIS) with Arduino add-on library. It can definitely run our test projects for this tutorial. But you won’t feel its power until you need some virtual test equipment like an oscilloscope, function generator, power supply, and advanced SPICE simulation for auxiliary electronic circuitry that you may build around an Arduino microcontroller.
Here is the Arduino project simulation result from the Proteus environment.
Check out the tutorial below to help you get started with simulating your Arduino projects in the Proteus simulation environment.
This article will provide you with more in-depth information about using proteus ISIS for Arduino projects simulation.
LED Fading Project Testing
Parts List
Here is the full components list for all parts that you’d need in order to perform the practical LABs mentioned here in this article and for the whole Arduino Programming series of tutorials found here on DeepBlueMbedded. Please, note that those are affiliate links and we’ll receive a small commission on your purchase at no additional cost to you, and it’d definitely support our work.
Download Attachments
You can download all attachment files for this Article/Tutorial (project files, schematics, code, etc..) using the link below. Please consider supporting my work through the various support options listed in the link down below. Every small donation helps to keep this website up and running and ultimately supports our community.
Project Wrap Up
To conclude this project tutorial, we can say that you can easily perform Fading LED Effects with Arduino PWM output using the analogWrite() function and a PWM output pin. To learn more about Arduino PWM, it’s highly recommended that you check out this Arduino PWM Tutorial. And check the Arduino projects page for more project ideas and code examples.
If you’re just getting started with Arduino, you need to check out the Arduino Getting Started [Ultimate Guide] here.
And follow this Arduino Series of Tutorials to learn more about Arduino Programming.
For more projects & ideas, check this Arduino Projects resource page.
This is the ultimate guide for getting started with Arduino for beginners. It’ll help you learn the Arduino fundamentals for Hardware & Software and understand the basics required to accelerate your learning journey with Arduino Programming.
FAQ & Answers
To make an Arduino Fading LED project, you need to use a PWM output pin.
1- Set it as an output pin using the pinMode function.
2- Make a for() loop to gradually increase the PWM’s duty cycle “Fade-in Effect”.
3- Make another for() loop to gradually decrease the PWM’s duty cycle “Fade-out Effect”.
To fade multiple LEDs with Arduino PWM output, you’ll need to use a switching device (like a BJT transistor or a MOSFET). This will help you drive a lot of LEDs all at once with the same PWM output pin from the Arduino. Note that you can’t drive multiple LEDs using only 1 IO pin from the Arduino. Because the pin can’t deliver more than 40mA and it’s going to be damaged if you over-drive it, and that’s why we need to use a transistor to drive multiple LEDs.
The LED light can be so dim due to using a high current-limiting resistor. You typically need to use a 220Ω or 330Ω resistors for this purpose. Another reason can be you’re connecting the LED to the wrong pin on the Arduino board, so double-check your connections. Sometimes it can be due to the fact that the LED’s ground lead is not properly connected, so make sure that the wiring is correct. Finally, you can test the LED without using Arduino IO pins to make sure that it’s not a damaged LED.
To Fade LEDs using PWM, you’ll have to gradually increase the PWM output’s duty cycle (Fade in effect). Then, gradually decrease the PWM’s duty cycle (Fade out effect). You can use two loops in Arduino alongside the analogWrite() function to achieve the LED Fading Effect.




