In this tutorial, we’ll create an STM32 LED Blink Example Code Project with the STM32 blue pill board. You’ll learn all the steps required to configure the STM32 microcontroller in CubeMX & flash the code from STM32CubeIDE to the blue pill board. Without further ado, let’s get right into it!
Table of Contents
STM32 LED Blink Overview
To create an STM32 LED Blink project, we need to configure a GPIO pin as an output pin and toggle its state at fixed time intervals.
For the GPIO pin state change, we can use one of the following functions:
- HAL_GPIO_Write() Sets an output pin to HIGH or LOW
- HAL_GPIO_TogglePin() Toggles the state of a GPIO pin
For the delay between each pin state change, we can use the following options:
- HAL_Delay() Built-in Function
- STM32 Hardware Timer Delay
- STM32 SysTick Timer Delay
- STM32 DWT Delay
The HAL_Delay() function is the easiest to use for such a project especially if it’s your first STM32 project. However, other time delay techniques are illustrated in more detail in the links above.
STM32 LED Blink Example
Objectives of This STM32 LED Blink Example Project:
- Configure GPIO Output Pin Within the STM32CubeMX Tool
- Use HAL_GPIO_Write() function to change an output pin state
- Use HAL_GPIO_TogglePin() function to toggle the state of a GPIO pin
- Use The HAL_Delay() & Know How It Works
Step #1
Open STM32CubeMX, create a new project, and select the STM32F103C8T6 target microcontroller. Note that the STM32 BluePill board has two common target microcontrollers (STM32F103C8T6 & STM32F103C6T6). So you need to select the exact target microcontroller on your hardware board.
This example project should work flawlessly on any STM32 target microcontroller, you just need to select the target MCU that matches your hardware board.
Step #2
Go to the RCC clock configuration page and enable the HSE external crystal oscillator input.
Click on the PA8 GPIO pin in the “Pinout View” and select it to be in GPIO_Output mode. Note: you can use any other pin you want instead.
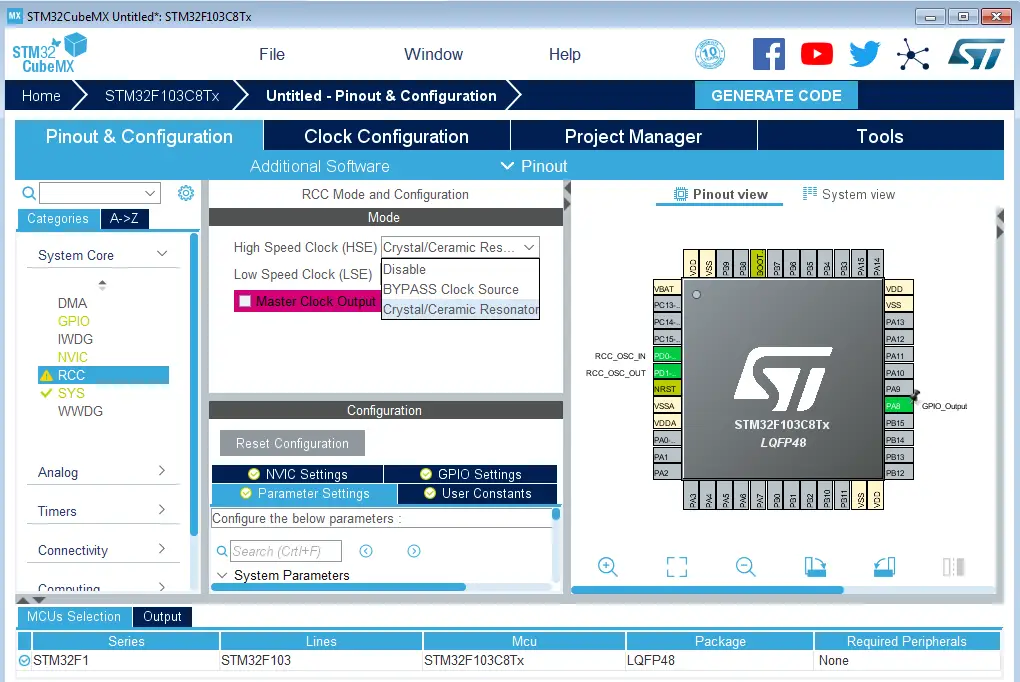
Step #3
Go to the clock configurations page, and select the HSE as a clock source, PLL output, and type in 72MHz for the desired output system frequency. Hit the “ Enter” key, and let the application solve for the required PLL dividers/multipliers to achieve the desired clock rate.
The reason behind this: using the external onboard oscillator on the BluePill board provides a more accurate and stable clock, and using a 72MHz as a system clock pushes the microcontroller to its limits, so we get the maximum performance out of it. As long as we don’t care about the application’s power consumption.
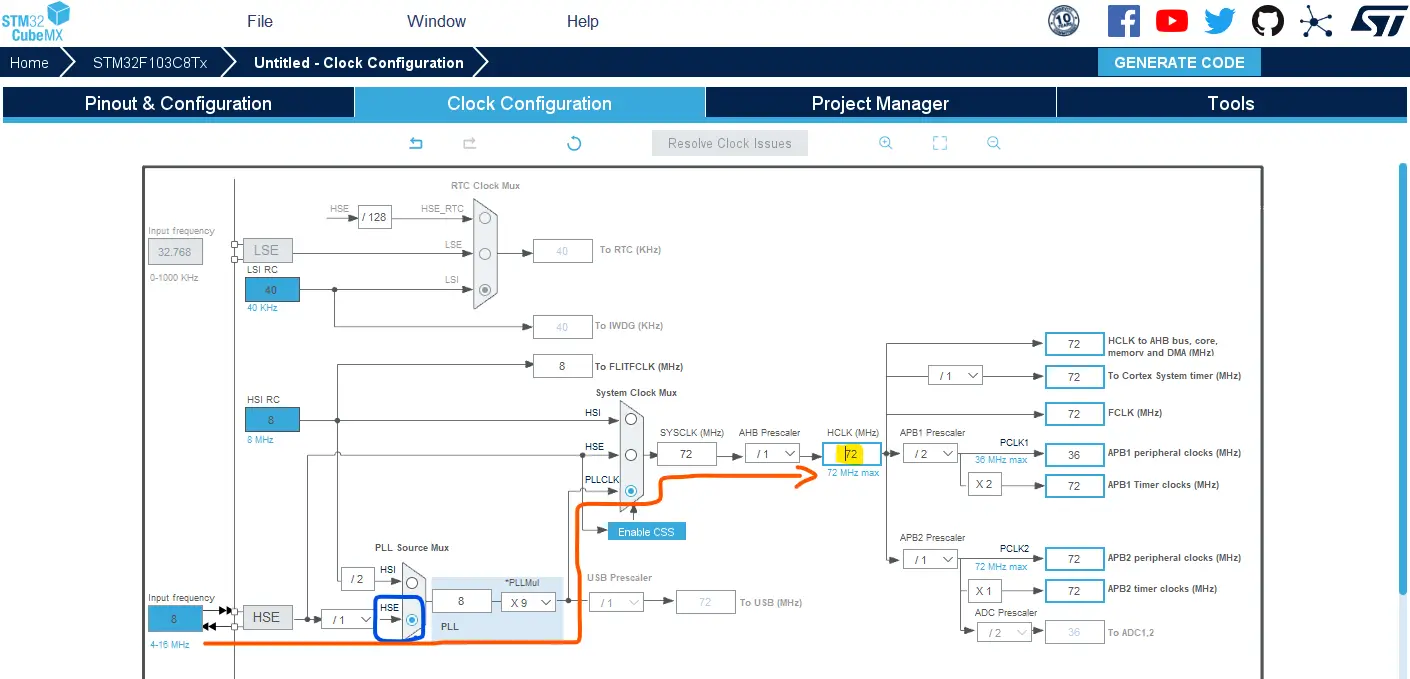
Step #4
Finally, go to the Project Manager, give your project a name, select the toolchain/IDE to be STM32CubeIDE, and click on the Generate Code button.
The STM32CubeMX tool will generate the initialization code & the project main files and it’ll prompt you to open the project in STM32CubeIDE. Select, open project, and let’s move to the next step.
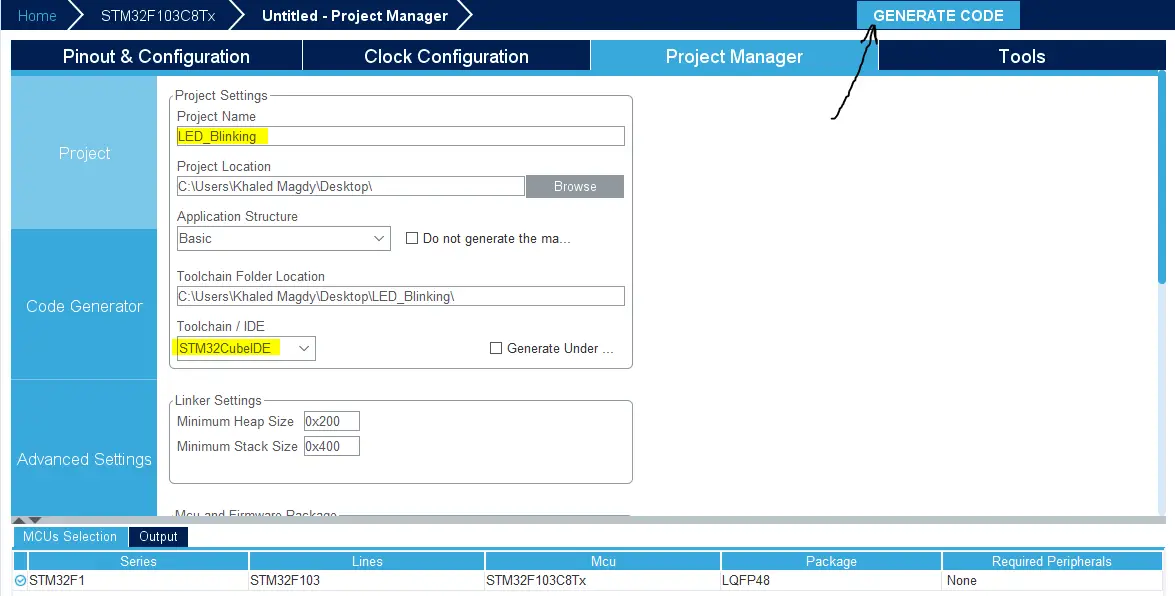
Then, open the project in the IDE you’re using. And head over to the main.c file. So we can start writing the application code and have a look at the initialization code generated by the STM32 CubeMX tool.
Step #5
Copy the following code into your main.c file replacing the auto-generated code from the beginning of the fill till the main function. You should leave everything else under the main() function in the main.c file as is.
STM32 LED Blink Example Code (HAL_GPIO_WritePin)
This code example uses the STM32 HAL_GPIO_TogglePin() function.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
#include "main.h" void SystemClock_Config(void); static void MX_GPIO_Init(void); int main(void) { HAL_Init(); SystemClock_Config(); MX_GPIO_Init(); while (1) { HAL_GPIO_TogglePin (GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_12); HAL_Delay (100); } } |
STM32 LED Blink Example Code (HAL GPIO Toggle Pin)
This code example uses the STM32 HAL_GPIO_TogglePin() function.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
#include "main.h" void SystemClock_Config(void); static void MX_GPIO_Init(void); int main(void) { HAL_Init(); SystemClock_Config(); MX_GPIO_Init(); while (1) { // LED ON HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_8, GPIO_PIN_SET); HAL_Delay(100); // LED OFF HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_8, GPIO_PIN_RESET); HAL_Delay(100); } } |
You can use any of the previous code examples. Both are doing the exact same functionality (blinking an LED every 100ms).
STM32 LED Blink Example Testing
Step #1
Refer To The Blue Pill Board Schematic & Pinout
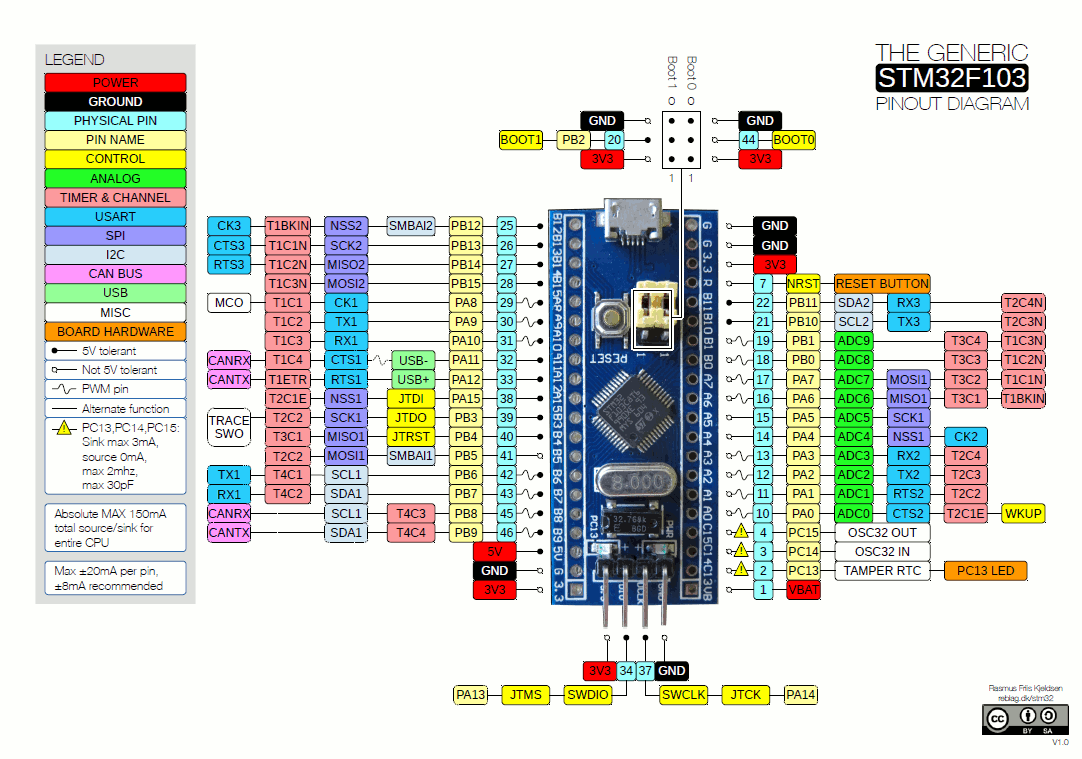
Step #2
Connect The ST-Link To The USB Port & SWD Pins On Board
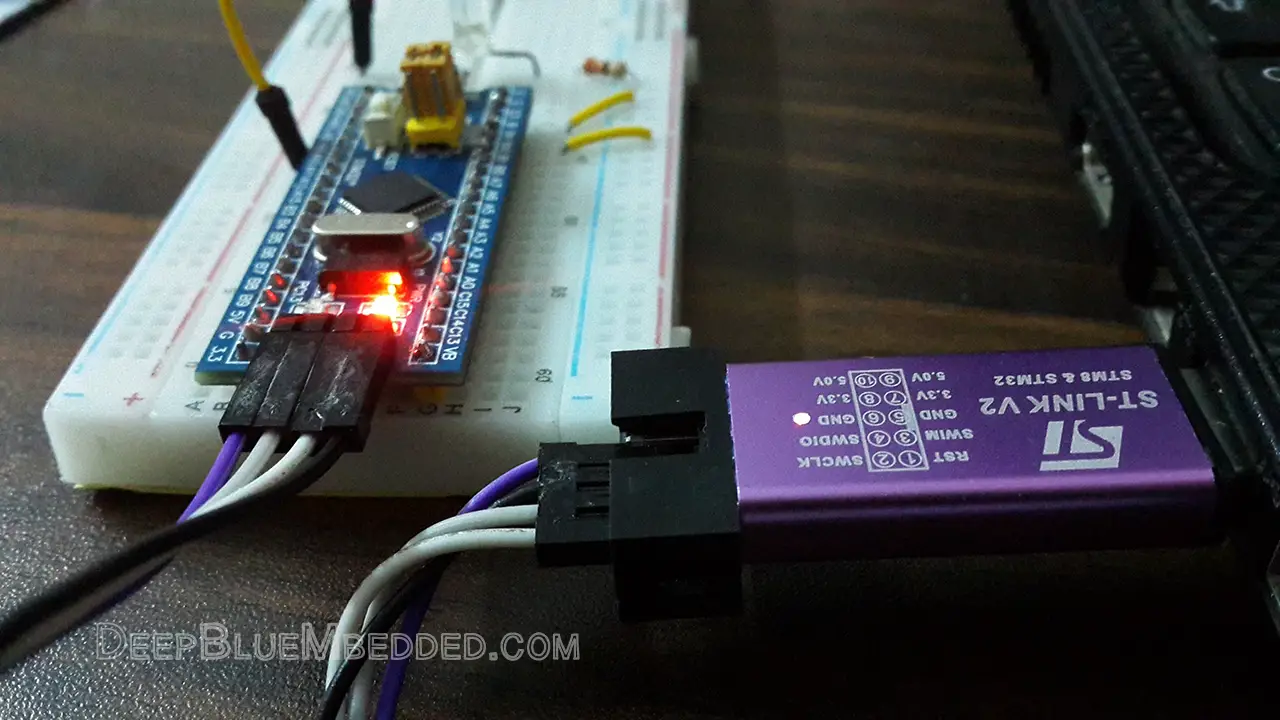
Step #3
Click The Debug Button To Compile The Code & Flash It To The Board & Start A Debugging Session
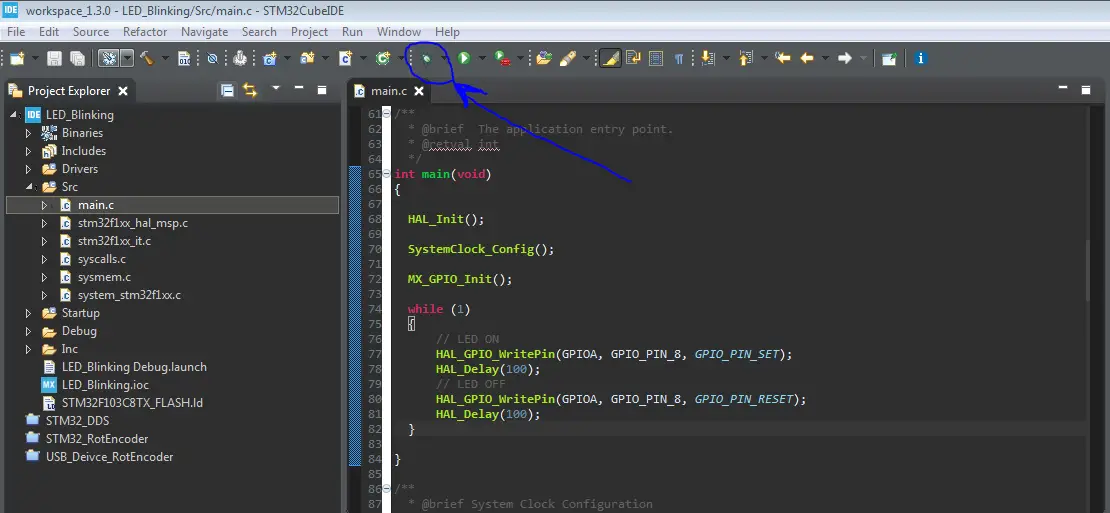
Step #4
You Can Stop The Debugging Session or Restart The MCU Once To Run The New Application At The Booting Process.
Required Parts For STM32 Examples
All the example Code/LABs/Projects in this STM32 Series of Tutorials are done using the Dev boards & Electronic Parts Below:
| QTY. | Component Name | Amazon.com | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | STM32-F103 BluePill Board (ARM Cortex-M3 @ 72MHz) | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Nucleo-L432KC (ARM Cortex-M4 @ 80MHz) | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | ST-Link V2 Debugger | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 2 | BreadBoard | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | LEDs Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Resistors Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Capacitors Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress & AliExpress | eBay & eBay |
| 1 | Jumper Wires Pack | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress & AliExpress | eBay & eBay |
| 1 | Push Buttons | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Potentiometers | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Micro USB Cable | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
★ Check The Links Below For The Full Course Kit List & LAB Test Equipment Required For Debugging ★
Download Attachments
You can download all attachment files for this Article/Tutorial (project files, schematics, code, etc..) using the link below. Please consider supporting our work through the various support options listed in the link down below. Every small donation helps to keep this website up and running and ultimately supports the whole community.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, it was quite easy to create our first STM32 LED blinking project using the HAL GPIO WritePin or TogglePin functions. You can play with different settings like delay period, multiple IO pins, and so on.
If you’re just getting started with STM32, you need to check out this STM32 Series of Tutorials to learn more about STM32 Microcontrollers Programming.

