In this tutorial, we’ll create an STM32 Serial Communication With PC example project. Using an STM32 With UART To USB TLL converter chip to send serial data from the STM32 microcontroller to the PC over UART. Without further ado, let’s get right into it!
Table of Contents
- STM32 Serial Communication With PC Example
- STM32 Communication With PC Example (UART To USB)
- Wrap Up
STM32 Serial Communication With PC Example
This is an overview of the steps for implementing this STM32 Serial Communication With PC example project using UART To USB converter:
- Configure GPIO input pin (for push-button) & output pins (for LEDs)
- Configure UART in asynchronous mode @ 9600 bps + Enable RX interrupts
- Read the button state and send it to the PC via the serial port
- Read the received characters from the PC and decide which LED to be toggled
STM32 Communication With PC Example (UART To USB)
The Blue Pill development board lacks an onboard ST-Link programmer/debugger, unlike Nucleo boards. That’s why we use the external USB ST-Link clone. And also it is worth mentioning that the USB port on the blue pill board is connected to the STM32F103C8 hardware USB peripheral. Therefore, it can actually be used for debugging but you’ll develop a USB application for it and it’s a topic for a future tutorial.
However, the UART peripherals in the microcontroller can be used to send serial data to the PC serial COM port and display it on a terminal using a USB-TTL converter board. Hence, you’re not restricted to using a specific UART module (UART1, UART2, or UART3).
The STM32F103C8 microcontrollers’ pins are not all 5v tolerant. Hence, you must be careful when receiving input signals from the USB-TTL converter. You can send a 3.3v signal from the MCU TX pin to the USB-TTL RX pin and still get the data identified absolutely fine.
However, it won’t work the other way around without shifting the signal’s level. The TX from the USB-TTL can over-drive the MCU’s RX input pin. By checking the diagram below, you’ll notice that the pins for UART1 & UART3 are 5v tolerant while UART2 is not.
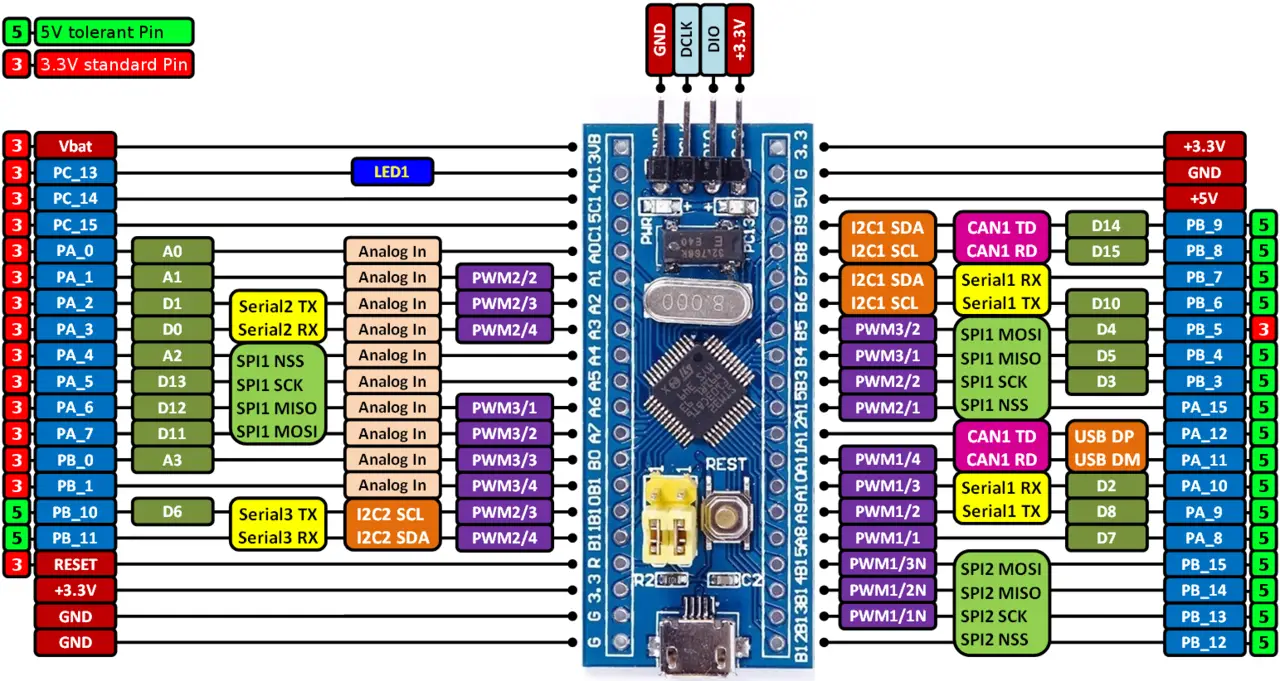
STM32 With UART-USB TTL Converter (Wiring)
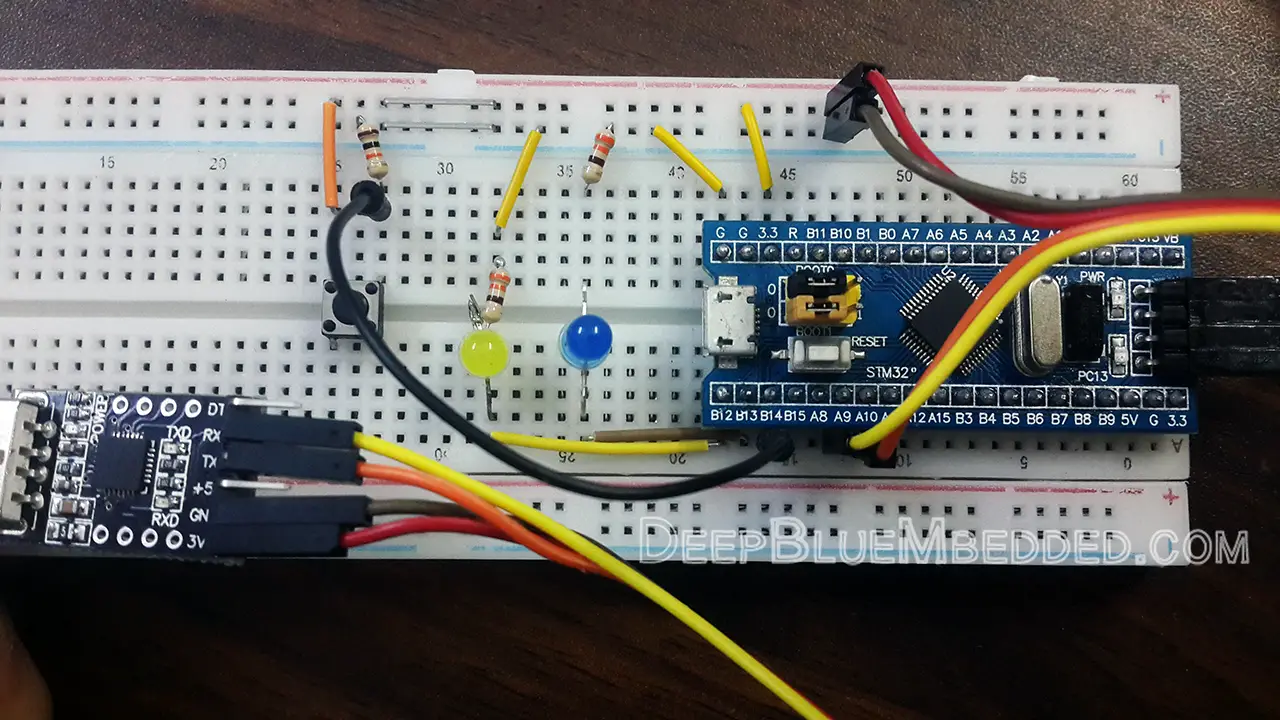
STM32 Serial Communication With PC (UART To USB) Code Example Project
Step #1
Open CubeMX & Create New Project
Step #2
Choose The Target MCU & Double-Click Its Name
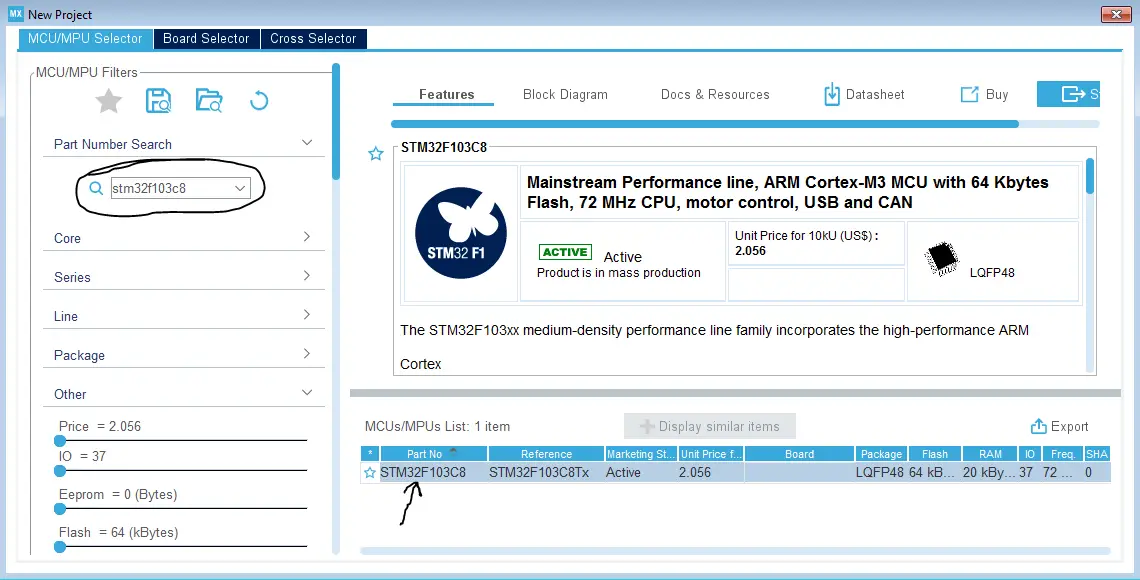
Step #3
Enable USART1 Module (Asynchronous Mode)
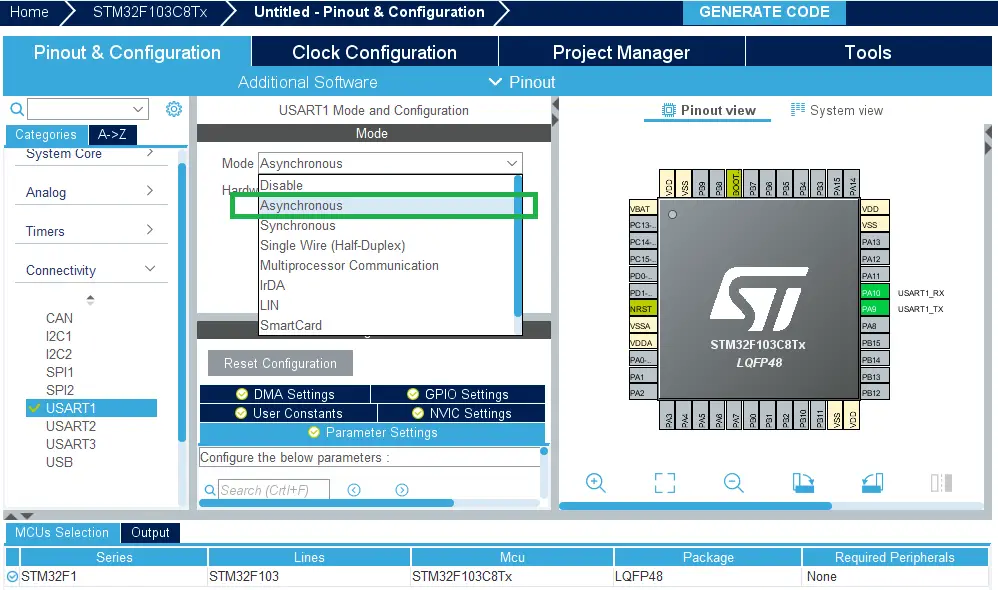
Step #4
Choose The Desired Settings For UART (Baud Rate, Stop Bits, Parity, etc..)
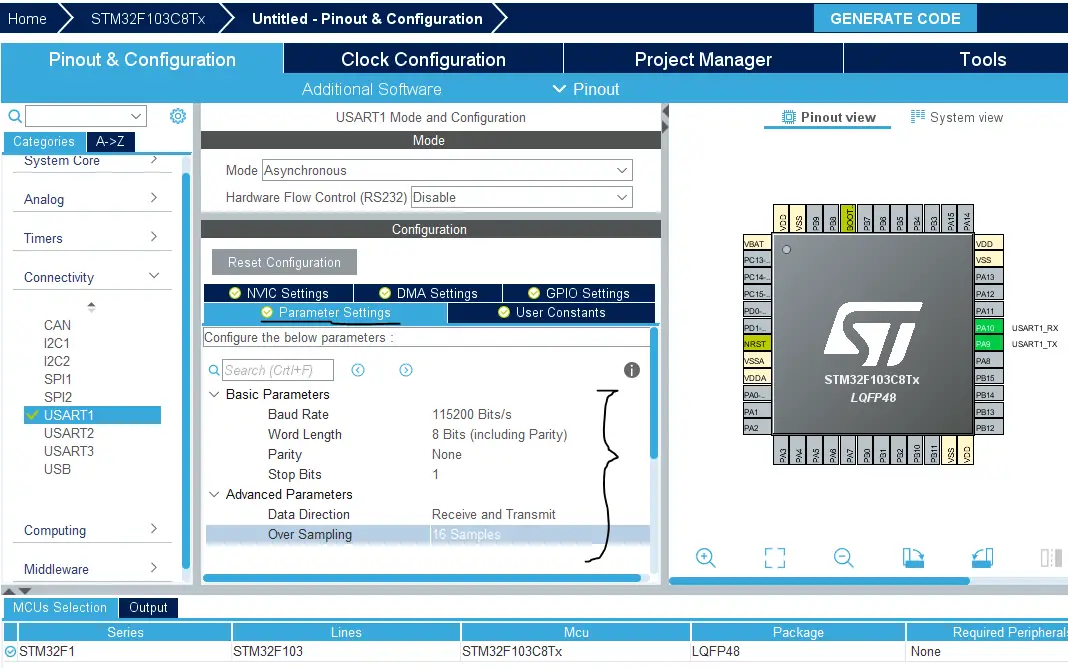
- Set the baud rate to 9600 bps
- Enable UART global interrupts in NVIC tab
Step #5
Configure The Required GPIO Pins For This Project
- PB12, PB13: Output Pins (For LEDs)
- PB14: Input Pin (For The Push Button)
Step #6
Goto The RCC Options Tab & Enable External Crystal
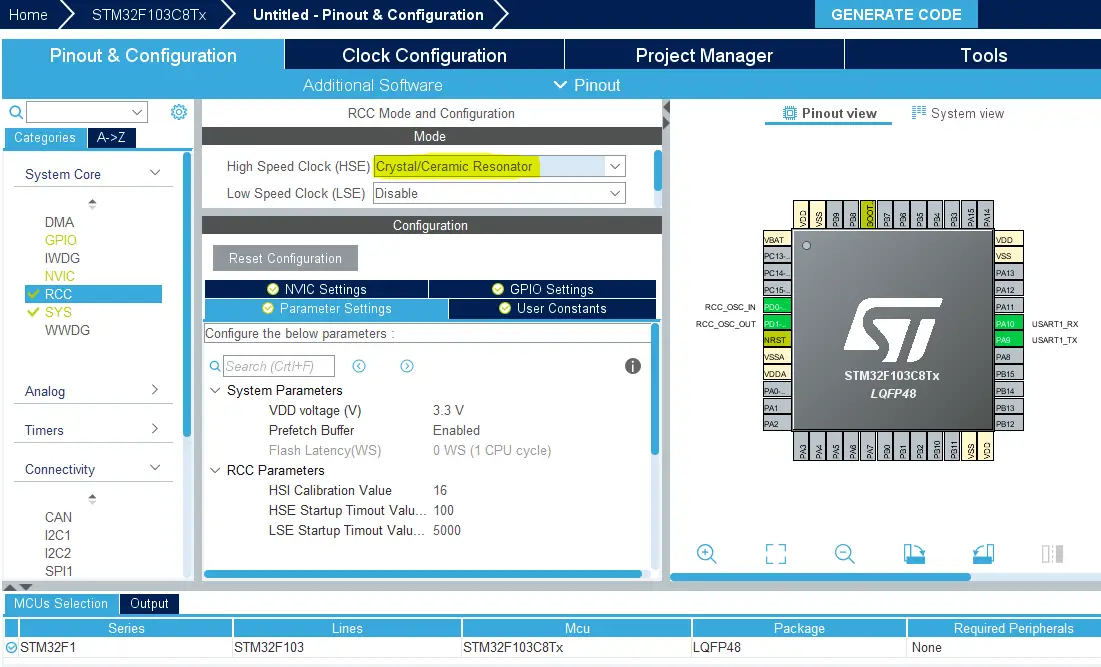
Step #7
Go To The Clock Configuration & Set The System Clock To 72MHz
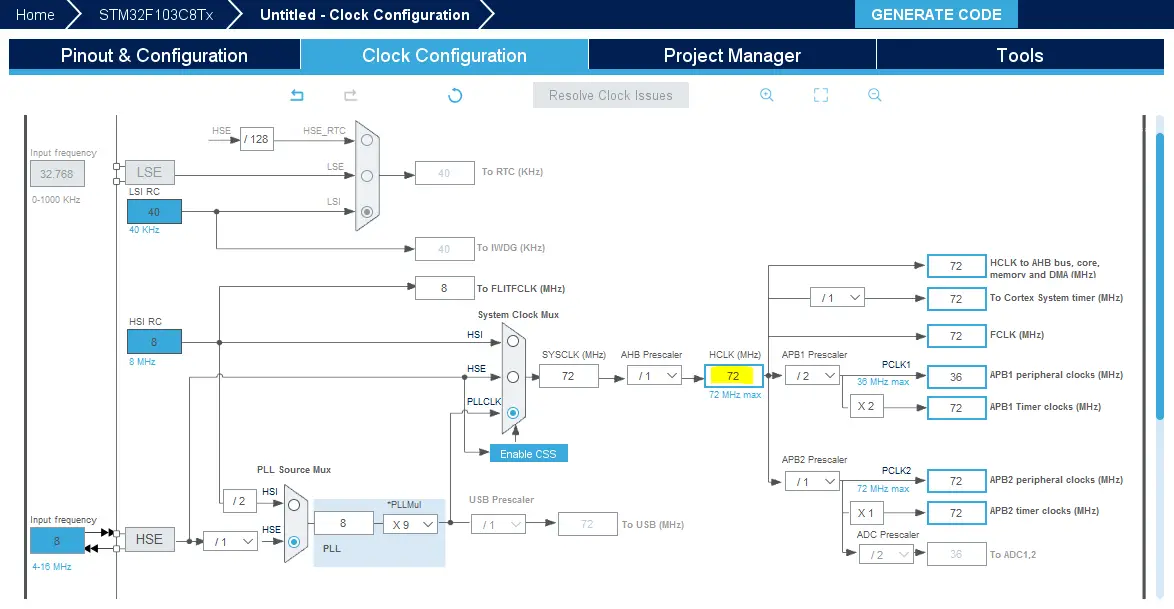
Step #8
Generate The Initialization Code & Open The Project In CubeIDE
Step #9
Write The Application Layer Code For This LAB
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 |
#include "main.h" UART_HandleTypeDef huart1; uint8_t RX1_Char = 0x00; void SystemClock_Config(void); static void MX_GPIO_Init(void); static void MX_USART1_UART_Init(void); //---------[ UART Data Reception Completion CallBackFunc. ]--------- void HAL_USART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart) { HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1, &RX1_Char, 1); } int main(void) { uint8_t MSG1[] = "Button State: Released\r\n"; uint8_t MSG2[] = "Button State: Pressed\r\n"; HAL_Init(); SystemClock_Config(); MX_GPIO_Init(); MX_USART1_UART_Init(); HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1, &RX1_Char, 1); while (1) { //--------[ Read The Button State & Send It Via UART ]--------- if(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_14)) { HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, MSG2, sizeof(MSG2), 100); } else { HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, MSG1, sizeof(MSG1), 100); } //--------[ Read The Received Character & Toggle LEDs Accordingly ]-------- if(RX1_Char == '1') { HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_12); HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1, &RX1_Char, 1); RX1_Char = 0x00; } if(RX1_Char == '2') { HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_13); HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1, &RX1_Char, 1); RX1_Char = 0x00; } HAL_Delay(100); } } |
Step #10
Build & Debug To Flash The Code
Step #11
Go To The Device Manager & Check The USB-TTL COM Port Num.
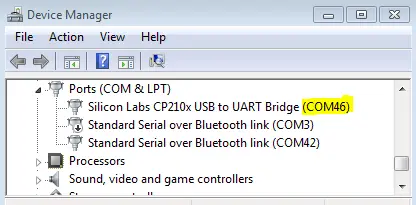
Step #12
Open The Terminal From CubeIDE or Any Other Terminal
Window > Show View > Console
In Console: click on the NEW icon on its menu bar > Command Shell console > Connection type: Serial port > set Baud Rate & Connection Name > Encoding: UTF-8 > And Click OK!
Alternatively, You Can Use Any Terminal On Your PC (Like Tera Term, Arduino Serial Monitor, etc..)
STM32 Communication With PC (UART To USB) Testing Demo
Required Parts For STM32 Examples
All the example Code/LABs/Projects in this STM32 Series of Tutorials are done using the Dev boards & Electronic Parts Below:
| QTY. | Component Name | Amazon.com | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | STM32-F103 BluePill Board (ARM Cortex-M3 @ 72MHz) | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Nucleo-L432KC (ARM Cortex-M4 @ 80MHz) | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | ST-Link V2 Debugger | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 2 | BreadBoard | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | LEDs Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Resistors Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Capacitors Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress & AliExpress | eBay & eBay |
| 1 | Jumper Wires Pack | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress & AliExpress | eBay & eBay |
| 1 | Push Buttons | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Potentiometers | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Micro USB Cable | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
★ Check The Links Below For The Full Course Kit List & LAB Test Equipment Required For Debugging ★
Download Attachments
You can download all attachment files for this Article/Tutorial (project files, schematics, code, etc..) using the link below. Please consider supporting our work through the various support options listed in the link down below. Every small donation helps to keep this website up and running and ultimately supports the whole community.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, we’ve explored how to set up an STM32 Serial Communication With PC using a UART To USB converter. This can be very useful for debugging your STM32 projects and visualizing data in runtime.
You can build on top of the example provided in this tutorial and/or explore the other parts of this STM32 UART tutorial series linked below.









Hi,
If I type random characters, callback (reading character) eventually doesn’t work anymore. What is the main reason ?
which terminal did you use? i cant do this. pls help