In this tutorial, we’ll discuss how the STM32 OpAmp (PGA) works, and how to use the STM32 OpAmp with ADC and enable the AWD (analog watchdog) to automatically amplify a current sensor’s reading voltage and trigger a warning signal when it goes out of the AWD voltage window.
The practical example project we’ll implement in this tutorial will be a very good starting point for your STM32 OpAmp-based project. Without further ado, let’s get right into it!
Table of Contents
- STM32 OpAmp (PGA)
- STM32 OpAmp + ADC Example (With AWD)
- STM32 OpAmp + ADC With Analog Watchdog Project
- Wrap Up
STM32 OpAmp (PGA)
The STM32 OpAmp peripheral is a hardware analog operational amplifier integrated inside the STM32 microcontroller itself. This opamp can be configured to operate in different modes which makes it so flexible and suitable for a wide range of applications.
It can also be referred to as PGA (Programmable Gain Amplifier) because it has an internal switchable array of resistors that allows programmatical change of the opamp’s gain using only software instructions.
STM32 OpAmp Main Features
- Rail-to-rail input and output voltage range
- Low input bias current (down to 1nA)
- Low input offset voltage (1.5mV after calibration, 3mV with factory calibration)
- Low-power mode (current consumption reduced to 30 µA instead of 100µA)
- Fast wake-up time (10µs in normal mode, 30µs in low-power mode)
- Gain bandwidth of 1.6MHz
STM32 OpAmp Modes of Operation
The STM32 OpAmp can be configured to operate in any of the following modes:
- Standalone OpAmp
- Voltage Follower OpAmp
- PGA OpAmp With (Vin-) Pin Exposed Externally
- PGA OpAmp With (Vin-) Pin Not Exposed Externally
| 1. Standalone OpAmp | 2. Voltage Follower OpAmp |
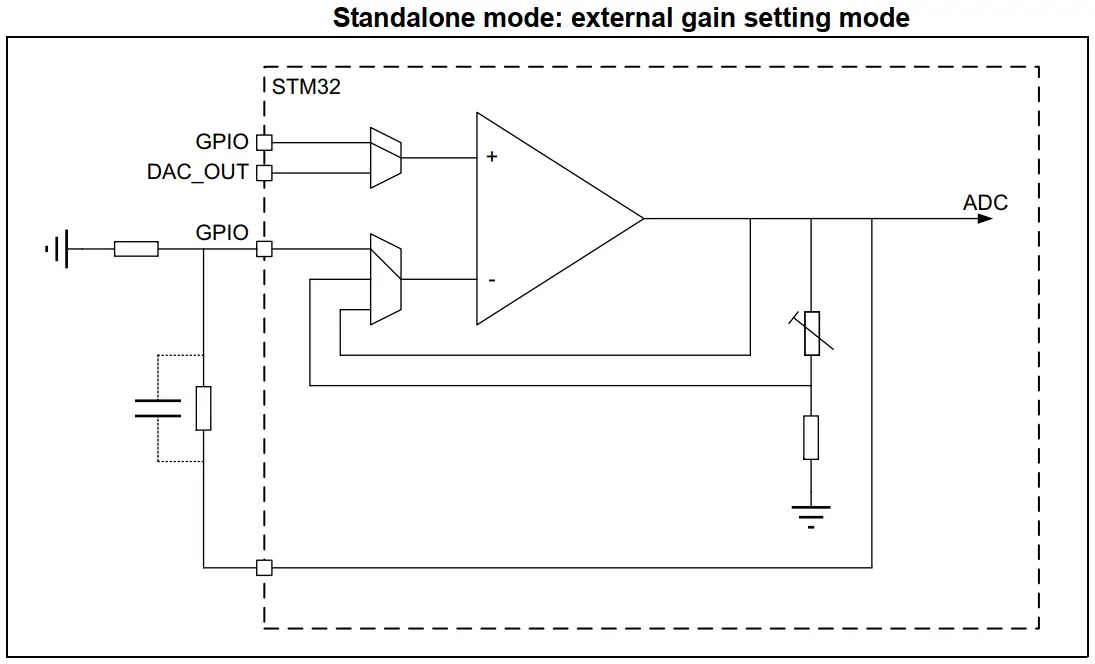 | 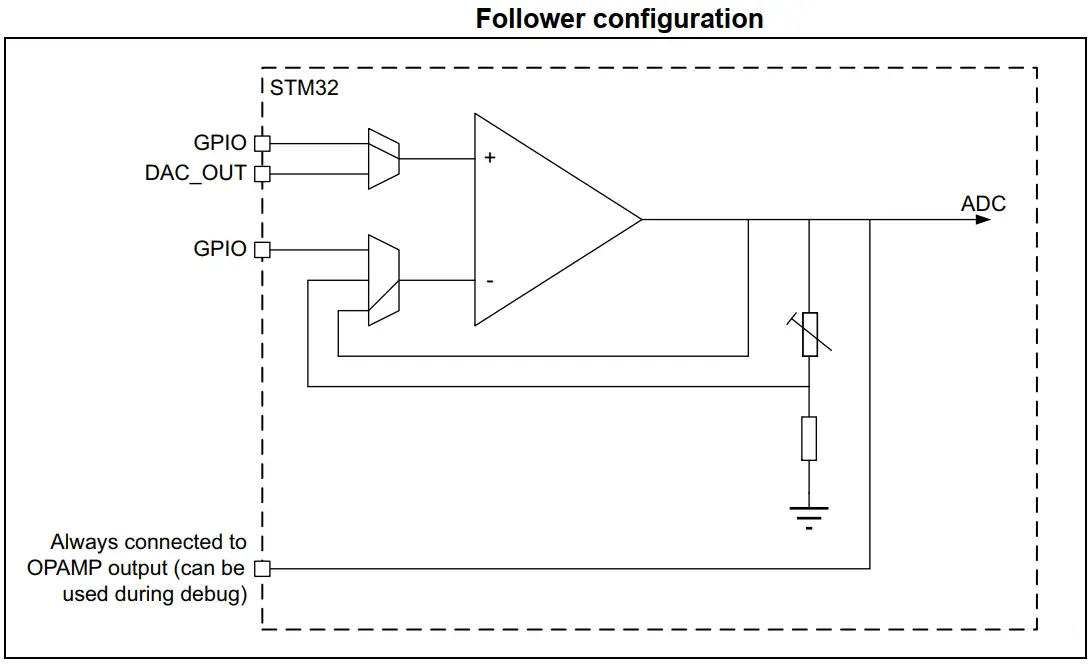 |
| 3. PGA OpAmp With (Vin-) Pin Exposed | 4. PGA OpAmp With (Vin-) Pin Not Exposed |
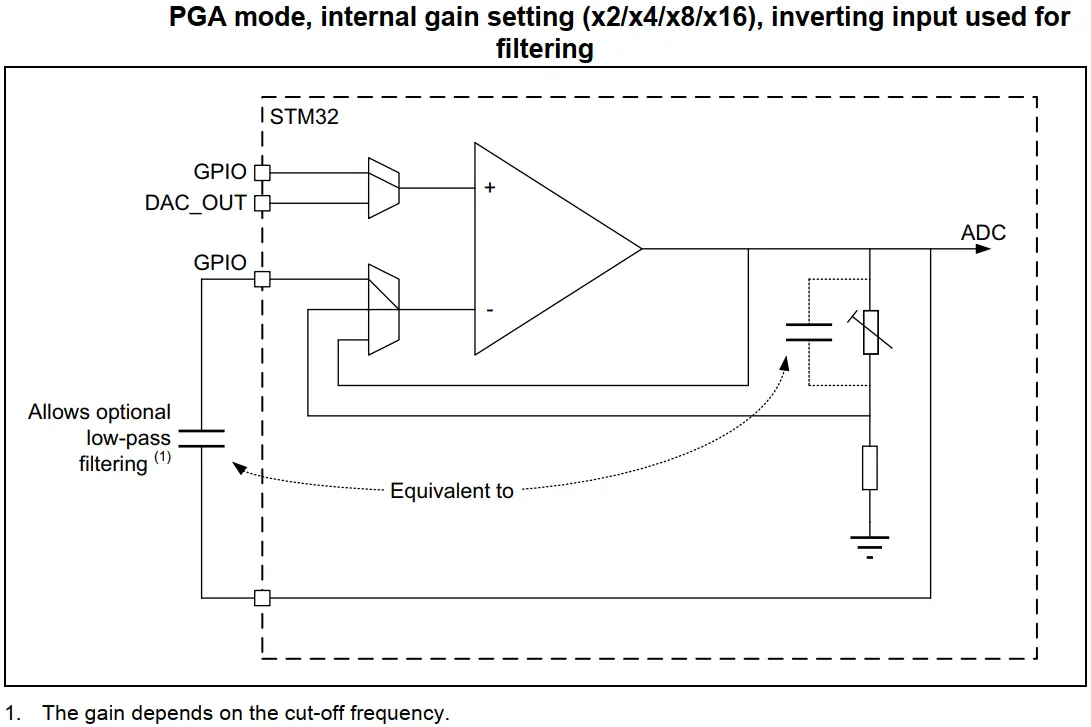 | 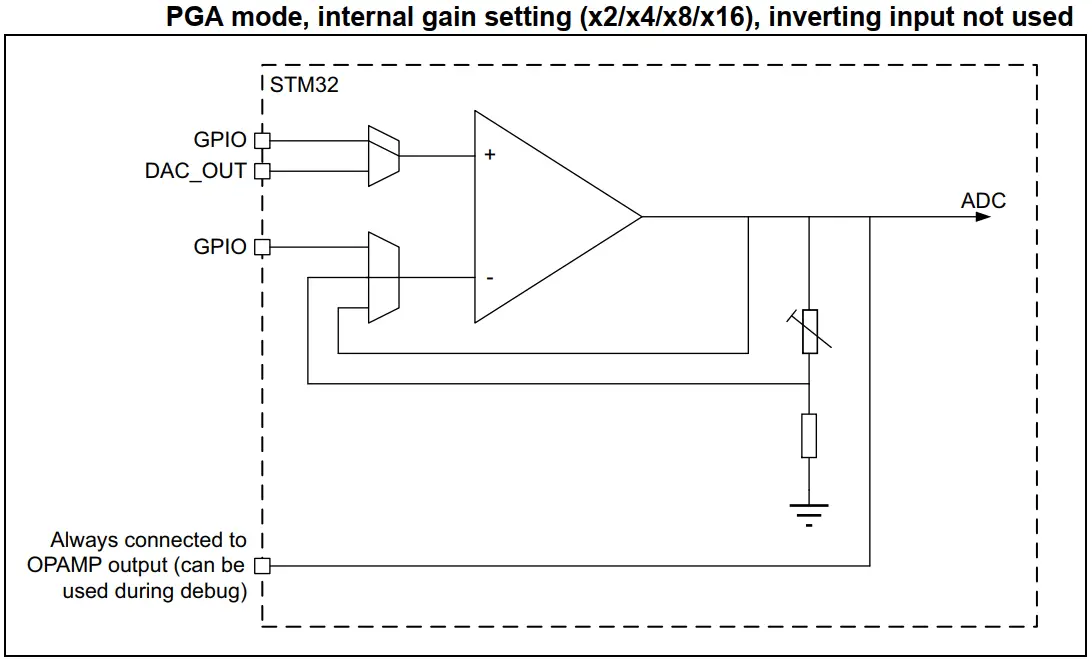 |
STM32 OpAmp Applications
The STM32 analog OpAmp can be used in so many applications and you can use it in many creative ways especially when configured as a standalone opamp. Here are some common applications for the integrated STM32 OpAmp peripheral:
- Sensor’s Signal Conditioning
- Analog Active Filters
- Analog Voltage Comparators
- Analog Oscillators
- Motor driver applications
- and much more…
STM32 OpAmp + ADC Example (With AWD)
In this example project, we’ll set up the STM32 OpAmp as a PGA (programmable gain amplifier) to amplify the voltage signal of a DC current shunt resistor (0.33Ω) used for measuring the current of whatever load. The voltage of the shunt resistor will be amplified by the internal opamp inside the STM32 microcontroller by a gain of (Gain=4).
The DC current going through the load is desired to have a limit of 0.5A. Therefore, we’ll route the internal opamp’s output to the ADC and configure this ADC’s channel AWD (analog watchdog) to monitor the output voltage of the opamp. When the VOUT of the opamp goes beyond VTH, a warning LED will turn ON indicating an “over current event” and the LED will turn OFF when the current goes back under the 0.5A limit.
Calculating the trip (VTH) voltage is relatively simple, we’ll just use the formula shown in the diagram below.
Example Project Wiring Diagram
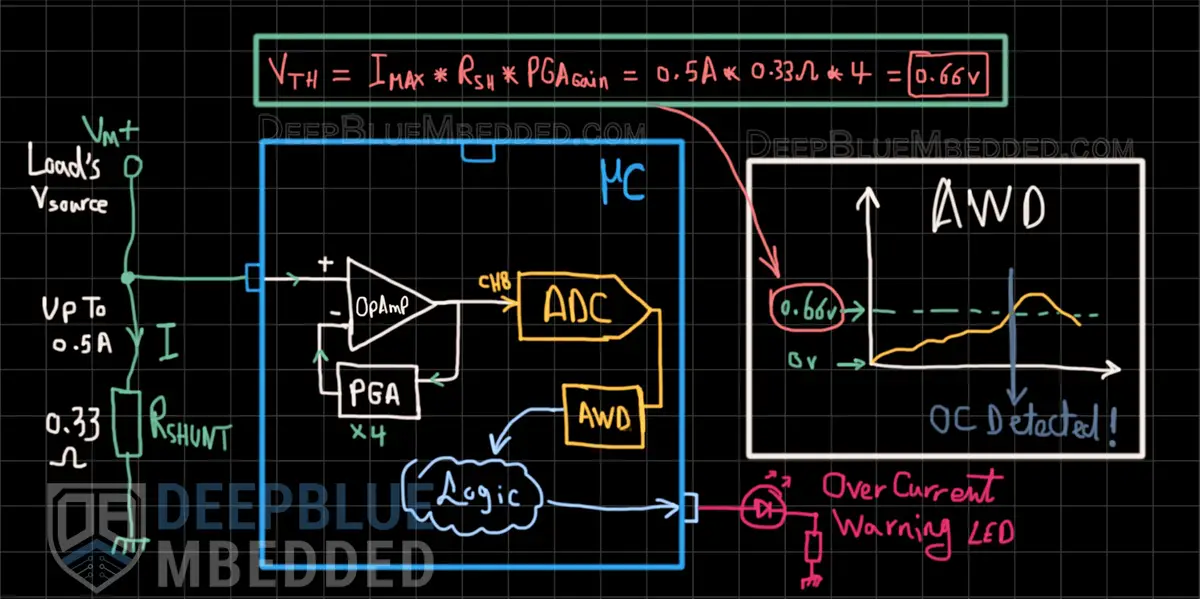
Example Project Steps Summary:
- Set up a new project, system clock, and enable SWD (serial wire debug)
- Set up 1x OpAmp in (PGA Not Connected) Mode
- Set up 1x GPIO pin: for the output indicator LED
- Set up 1x ADC channel and route the OpAmp’s VOUT to it and enable the AWD to have a window of (0 – 820) which corresponds to (0v – 0.66v)
This article will give you more in-depth information about the STM32 ADC Analog Watchdog feature, how it works, and how to use it in practical projects with a couple of examples & test codes.
STM32 OpAmp + ADC With Analog Watchdog Project
And now, let’s build this system step-by-step
Step #1
Open STM32CubeMX, create a new project, and select the target microcontroller.
Step #2
Set the 1x GPIO B7 as an output pin (for the indicator LED)
Step #3
Enable OpAmp1 to operate in the PGA Not Connected mode. Set the gain value to 4 as shown below.
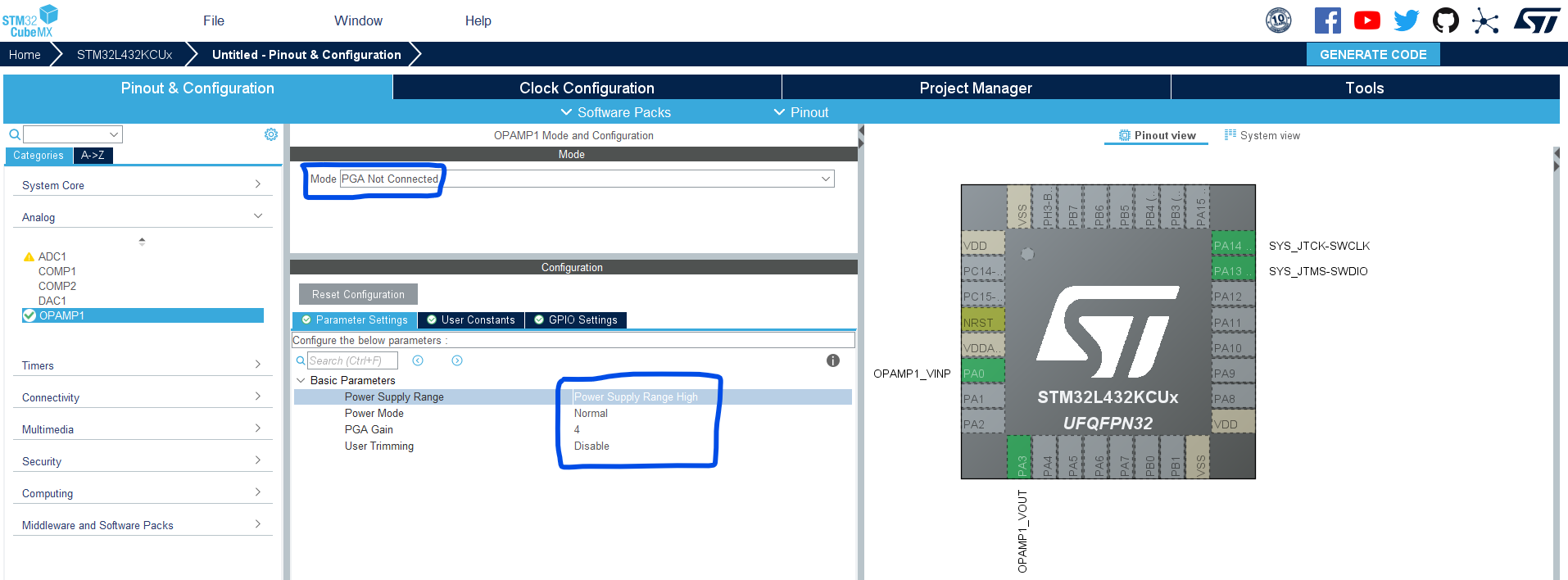
Step #4
Go to the ADC1, and enable CH8 to operate in OpAmp1 Out Single-Ended mode to route the opamp’s output internally to this ADC’s channel.
Enable The AWD1 (Analog Watchdog1) for CH8, and set the HIGH Threshold to 820 (which corresponds to 0.66v). Note that: (820/4095) * 3.3v = 0.66v
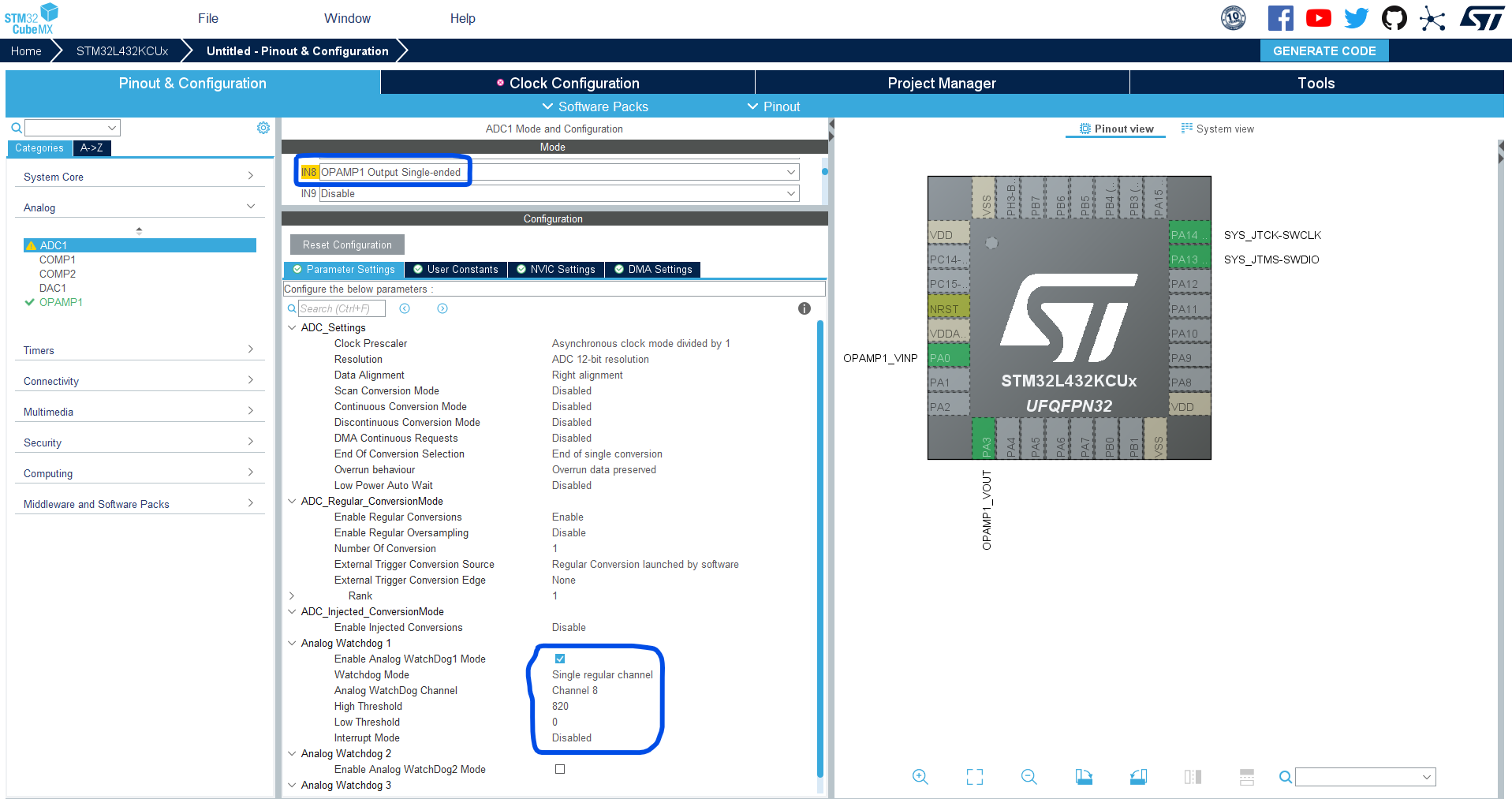
Step #5
Set up system clock, and enable SWD (serial wire debug).
Name & Generate The Project Initialization Code For CubeIDE or The IDE You’re Using.
STM32 (PGA+ADC+AWD) Example Code
Here is The Application Code For This LAB (main.c)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
/* * LAB Name: STM32 OpAmp PGA + ADC + Analog Watchdog Example * Author: Khaled Magdy * For More Info Visit: www.DeepBlueMbedded.com */ #include "main.h" ADC_HandleTypeDef hadc1; OPAMP_HandleTypeDef hopamp1; void SystemClock_Config(void); static void MX_GPIO_Init(void); static void MX_ADC1_Init(void); static void MX_OPAMP1_Init(void); int main(void) { HAL_Init(); SystemClock_Config(); MX_GPIO_Init(); MX_ADC1_Init(); MX_OPAMP1_Init(); HAL_OPAMP_Start(&hopamp1); while (1) { HAL_ADC_Start(&hadc1); if(HAL_ADC_PollForEvent(&hadc1, ADC_AWD1_EVENT, 1) != HAL_TIMEOUT) { HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_7, 1); } else { HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_7, 0); } } } |
STM32 PGA+ADC+AWD Example Testing
You’ll most probably need to modify the VTH value to suit your application according to: the shunt resistor’s (RSHUNT) value you’re using, the PGA Gain setting, and the desired maximum current (IMAX) at which you want to trigger the warning signal.
Required Parts For STM32 Examples
All the example Code/LABs/Projects in this STM32 Series of Tutorials are done using the Dev boards & Electronic Parts Below:
| QTY. | Component Name | Amazon.com | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | STM32-F103 BluePill Board (ARM Cortex-M3 @ 72MHz) | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Nucleo-L432KC (ARM Cortex-M4 @ 80MHz) | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | ST-Link V2 Debugger | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 2 | BreadBoard | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | LEDs Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Resistors Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Capacitors Kit | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress & AliExpress | eBay & eBay |
| 1 | Jumper Wires Pack | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress & AliExpress | eBay & eBay |
| 1 | Push Buttons | Amazon & Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Potentiometers | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
| 1 | Micro USB Cable | Amazon | AliExpress | eBay |
★ Check The Links Below For The Full Course Kit List & LAB Test Equipment Required For Debugging ★
Download Attachments
You can download all attachment files for this Article/Tutorial (project files, schematics, code, etc..) using the link below. Please consider supporting our work through the various support options listed in the link down below. Every small donation helps to keep this website up and running and ultimately supports the whole community.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, we’ve explored how the STM32 OpAmp works, what are the possible operating modes that you can configure it to, and how to route the OpAmp’s output voltage internally to an ADC channel and activate the AWD (analog watchdog) for automated voltage level monitoring.
You can build on top of the example provided in this tutorial and/or explore all of our STM32 Tutorials.